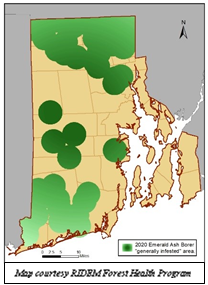
Emerald Ash Borer Continues to Spread Across Rhode Island
The Department of Environmental Management (DEM) reports that Emerald Ash Borer (EAB), a destructive forest insect from Asia, continues to spread throughout Rhode Island.
EAB overwinter as larvae under the bark of ash trees where they feed on the inner bark tissue. Once infested, ash trees rapidly decline and can be killed in as few as three to five years.
This pest is responsible for widespread decline and
mortality of hundreds of millions of ash trees in North America.
EAB threatens all ash species in Rhode Island, including white ash, green ash and black ash. Ash trees comprise approximately one to two percent of Rhode Island forests, and are a common urban tree because of their hardiness, tolerance to pollutants, and for the shade they provide.
At present there are no proven
methods to control EAB in forested areas, though individual landscape trees can
be treated.
Research
into control efforts continue, including parasitoid insects, such as the
parasitic wasps being released by the University of Rhode Island (URI). If a
population of these wasps establishes successfully, they could help slow the
spread of EAB, buying time for the research efforts into genetic research into
the small number of ash trees that have survived EAB infestation. Ongoing
genetic research on these "lingering ash" may be key to the survival
of the species.
While adult EAB can fly short distances, humans have hastened their spread by moving infested material, particularly firewood.
The most effective way to slow the
spread of EAB is to follow the recommendations of the "Don't Move
Firewood" program. Residents and visitors are reminded to protect Rhode
Island's forests by buying and burning local firewood.
To address the destructive effects of EAB to Rhode Island's ash resources, DEM finalized an action plan in 2019 in partnership with URI, National Grid, USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service, and the USDA Forest Service State & Private Forestry.
DEM's Divisions of Agriculture and Forest Environment, in cooperation with project partners, are using the EAB Technical Response Plan to guide Rhode Island communities, homeowners, woodland property owners, and other stakeholders that may be affected by EAB.
The guidance document is also
used to assist RI landowners and municipalities in raising awareness of EAB and
other invasive pests, how to identify and inventory ash trees, and how to
minimize risks. DEM and URI continue to survey for EAB to determine the extent
of the EAB infestation. Results of the surveys will inform subsequent
management decisions.
For
more information on Emerald Ash Borer or other exotic agricultural pests,
invasive insects, or plants, please visit DEM's website.
To
report a suspected exotic or invasive insect or plant, please fill out the DEM
Invasive Species Reporting Form, which is posted on DEM's website.
For
more information on DEM programs and services, visit www.dem.ri.gov. Follow DEM
on Twitter (@RhodeIslandDEM) or Facebook at www.facebook.com/RhodeIslandDEM for
timely updates.
Related
links