Climate & French fries
By
Michon Scott
 |
| Fries please foodies when they involve garlic, truffles, and parsley. CC license by Flickr user L.A. Foodie. |
Named for its hot dogs, “The O,” as it was often called, was arguably better known for its fries. Cooked twice in peanut oil (first at low heat to cook the inside, again at high heat to crisp the outside),
The O’s famous fries—featured in a 1999 PBS documentary—came in
portions big enough to satisfy several people, even without hot dogs.
Whether
at The O, a chain restaurant, an upscale eatery, or home, we Americans love our
fries. According to a recent study cited by the Washington State University
Potato Research Lab, the average American consumes 34 pounds of French fries
each year.
Fries depend on potatoes, and like all crops, potatoes have a preferred climate. How long will America’s favorite side dish have a safe spot on our menu?
From farm to fry basket
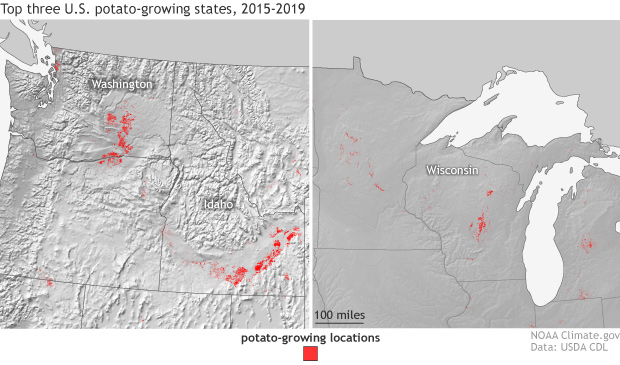
First cultivated in South America as much as 10,000 years ago, potato plants grow over most of Earth’s land surfaces, though most production now occurs in the Northern Hemisphere. The top U.S. producers are Idaho and Washington.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture reports that in 2017, Idaho produced around 13.5 billion pounds of potatoes, and Washington produced close to 10 billion pounds. In third place was Wisconsin, with just under 3 billion pounds.
Purple
potato flowers bloom in profusion in Peru, one of the first places where this
tasty tuber was cultivated. CC license by Flickr user Leonora (Ellie) Enking.
Third
in volume, Wisconsin comes first in variety. According to Tamas Houlihan,
executive director of the Wisconsin Potato and Vegetable Growers Association,
Wisconsin grows more kinds of potatoes than any other state. About 20 percent
of Wisconsin’s potatoes turn into French fries. Planting usually begins in
early April and ends in late May. Tubers (the parts we like to eat) begin to
form in June, and keep growing in July. Major commercial potato harvests occur
in the relatively cooler months of autumn.
The
top three potato-growing states in the United States are Idaho, Washington, and
Wisconsin. Although Wisconsin is a distant third, it produces the greatest
variety of potatoes. Maps by NOAA Climate.gov based on data from USDA CDL.
“September
and October are the primary harvesting months for the major production regions
of the United States,” Houlihan says. “As those potatoes are harvested, some
will go directly by truck to the factory. Once there, they are weighed and
graded and sorted into different sizes. Some of those potatoes are processed
immediately and turned into French fries.”
Other
potatoes, Houlihan says, go into storage, able to be turned into fries later.
“We now have learned how to store potatoes for almost a full year.” The most
popular potato type for French fries is the Russet, especially the Russet
Burbank. “I think the ideal storage temperature for a Russet Burbank is
45°F–48°F-degrees. You’ve got to be able to maintain that for up to nine
months. You also need very high humidity, above 90 or 95 percent.”
Large commercial growers, who often operate their own storage facilities, continually refine their buildings and protocols. “We’ve found if we put culverts and fresh air in storage facilities, potatoes do better and can last longer,” Houlihan says. Houlihan notes that many growers have adopted cement floors and even cement walls to nudge temperatures lower and maintain high humidity.
Multiple heat hazards
Although
they can grow in a lot of places, the fungus-fouled tuber that famously failed
Ireland in the mid-19th century is largely a cool-weather crop. A 2019 study
in Breeding Science reported that the optimum
temperature for potato vegetative growth—above-ground stems and leaves—is a
relatively cool 75°F (24°C), but the maximum tuber yield
occurs at an even cooler 68°F (20°C). Combine that with the need for months of
cold storage, and it’s clear why the nation’s top potato states are in the
northern tier of the country.
It’s
also clear why global warming might pose hazards for French fries.
One hazard involves starches and sugars. Russet Burbank potatoes fry well due to their high starch content. According to Richard Novy, a research geneticist with the Agricultural Research Service at the U.S. Department of Agriculture in Aberdeen, Idaho, the key is retaining the starch as long as possible, reducing its conversion to glucose and fructose.
In Russet Burbank potatoes, higher temperatures can cause an uneven starch-to-sugar conversion. “With that, when you fry it up then, you can have something called sugar ends. You have a nice, light fry except at the very end, where it’s sort of darker brown,” he says. Big producers of French fries have exacting standards that brown sugar ends don’t meet.
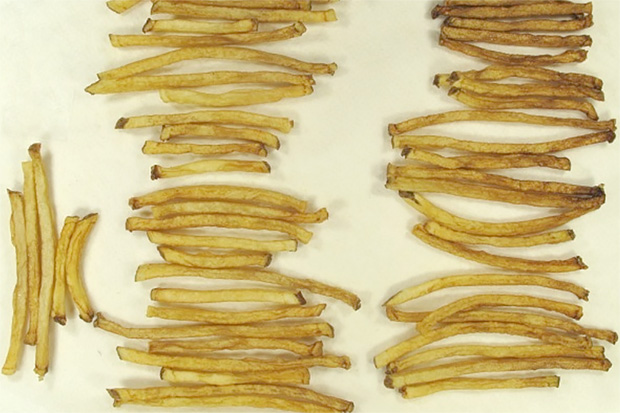
Russet
potatoes are vulnerable to “sugar ends”: burnt-looking tips of French fries.
Fries in the right half of this photo exhibit the problem potato producers try
to avoid. Image from Zhu et al. 2015 in PLoS ONE, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093381.g003.
Another
problem, Novy says, is second growth. “If you have high heat for extended
periods, and you’re not able to put on adequate water during that period, you
can get protuberances or bumps or knobs. They can result from the interaction
between heat and water. The Russet Burbank tends to be a little more sensitive
than other varieties to second-growth malformations.”
Changing climate also brings changing threats of potato-plant disease. Like Rich Novy, Dennis Halterman is a USDA ARS research geneticist, but he works from an office in Madison, Wisconsin. Halterman explains that most potato pathogens have favorite temperature ranges.
Late blight—the culprit behind the Irish potato
famine—prefers cool temperatures (65˚F–68˚F), whereas verticillium wilt—another
fungal disease pestering potatoes—prefers warmer temperatures (80˚F–85˚F). As
climate warms, he notes, disease risks will shift.
Halterman also recently collaborated on research showing that potatoes can lose their ability to fight disease at higher temperatures. Between temperatures of 68˚F and 75˚F, the Premier Russet resists some varieties of a pathogen called Potato Virus Y. But when temperatures rise above 82˚F, that resistance falters.
“We
aren’t exactly sure how this happens, but we know that it has something to do
with how the potato plants respond to the virus and how they defend themselves
against infection. At an elevated temperature, they aren’t able to mount an
effective defense to stop the virus from spreading,” he writes in an email.
Warming
climate is likely to bring yet another threat: an expansion in the range of the
Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa
decemlineata. A 2017 study examined the relationship between
the pest, its original host plant—Solanum rostratum, sometimes
called spiny nightshade—and climate, concluding that
climate change would expand the habitat suitable for the beetle into new parts
of the Northern Hemisphere, in part because the host plant will thrive in those
areas.
Past and future changes in temperature
Across most of the United States, warming is well underway. The 2018 National Climate Assessment (NCA) reported that annual temperatures from 1986–2016 increased relative to 1901–1960 over most of the contiguous United States, including Idaho, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Over the past 30 years, potato-growing parts
of eastern Washington and southern Idaho have experienced some of the country’s largest increases in
daytime high temperatures in summer. At the peak of the summer heat in
July, average daytime
highs across parts of central Wisconsin have been rising by
more than 1.5°F per decade. Along Idaho’s Snake River Plain, the state’s
agricultural heartland, daytime highs in July have warmed by more than 2°F per
decade.
If the world follows an energy pathway that leads to high carbon dioxide emissions, these trends will continue, pushing summertime temperatures even further away from potatoes’ optimum conditions. According to the U.S. Climate Explorer, under a higher-emissions scenario, models project that by the 2050s, the number of days with extreme heat—daytime highs above 90°F—will likely more than double compared to the 1961–1990 average in many potato-growing parts of Washington, Idaho, and Wisconsin.
Water: too little or too much?
In
addition to their preference for cool temperatures, most modern potato
varieties—with their relatively shallow root systems that thrive in sandy,
loose soils—have low tolerance for drought. According to a 2013 study in Plant Science, climate change is likely to increase
drought risks to potato crops in many potato-growing regions of the world over
the 21st century.
“Most
of Wisconsin’s potatoes are grown in the state’s Central Sands region, which is
an ideal environment for ample water supply,” says assistant Wisconsin state
climatologist Edward Hopkins. He explains that some of Wisconsin’s prime
potato-growing counties were once home to a glacial lake, which left behind an
expanse of sandy soils.
“In
Wisconsin we’re fortunate in that we get about 30 inches of precipitation a
year. So, throughout the growing season, we typically get enough rain to keep
the potatoes healthy. Now, 99 percent of our growers have irrigation systems
just to make sure,” Houlihan says.
In
Idaho and Washington, meanwhile, irrigation isn’t a backup, it’s a necessity.
Potato production in Idaho is concentrated in the southern and eastern portions
of the state; production in Washington is concentrated in the eastern half of
that state. Both places are much drier than famously rainy Seattle or Portland.
Reliance on irrigation has an upside, says the USDA’s Novy. In the northwestern United States, annual precipitation in potato-production regions can be less than 12 inches per year, and heavy rainfall events are rare, especially during the potato-growing season.
“But as long as you have enough water to irrigate, you generally have very high-quality potato crop just from the standpoint that you are the one controlling the water that goes onto that crop. You don’t have Mother Nature throwing a monkey wrench into that production,” he says. But reliance on irrigation has a downside, too. Population growth in the western half of the United States places increasing demands on scarce water resources. “If water becomes more limited, that creates issues for future production.”
Though drought is less likely in Wisconsin than in western states, Houlihan says, it still happens. But for all the damage drought can cause, Houlihan worries more about another issue: too much water. “We had a disaster in 2018,” he says.
That
year, waterlogged potato fields prohibited growers from harvesting for weeks.
Harvesters that collect potatoes on an industrial scale weigh tons. In soil
that’s too moist, they simply sink. “By the time they got into their fields, it
was October and we had an early frost. It just devastated the crop.”
Past and future changes in precipitation
According
to the National Climate Assessment, between 1986–2015, annual precipitation
declined over much of the western half United States and increased over much of
the eastern half relative to the period from 1901–1960. But conditions vary
substantially from place to place and season to season.
In
the past three decades, spring precipitation has risen slightly across parts of
Washington and Idaho where potatoes are widely grown, while summer
precipitation has declined. For the most part, however, these changes are small
compared to the range of natural variability.
Calculating
precipitation trends for Central Wisconsin since 1961, climatologist Hopkins
has found a 23-percent increase in spring precipitation, and a 24-percent
increase in summer precipitation. Most years, potatoes fare just fine, but like
all plants, they can get too much of a good thing. “In sandy soil, water can
saturate up, and where does it go? It comes out of the ground. And potatoes
don’t want to get their feet wet.”
According to projections of future precipitation in the National Climate Assessment, wet feet will be a bigger concern in some seasons than others. If the world follows a pathway with high greenhouse gas emissions, Washington and southern Idaho are likely to see a 5–10-percent increase in spring precipitation by the end of the century, a relatively small change compared to the area’s natural year-to-year variability.
But in potato-growing parts of Wisconsin, spring precipitation may
increase by a more significant 15–20 percent. Falls may get a tiny bit wetter,
too, though again, the projected changes are small relative to natural
variability. In summer, the pattern diverges, with small declines
projected for Wisconsin and southern Idaho, and more serious declines (up to
15–20 percent) in parts of Washington.
These
maps show predicted changes in precipitation for spring and summer in the late
21st century under a high-emissions scenario (RCP8.5). Increased precipitation
appears in shades of blue-green. Reduced precipitation appears in shades of
brown. Red stipples indicate strong confidence in changes. Hatch marks indicate
small anticipated changes relative to natural variability. Adapted from U.S.
National Climate Assessment, 2018.
But as Dan McEvoy of the Western Regional Climate Center points out, crop stress may increase considerably in summer even without significant declines in rainfall. McEvoy coauthored a study on irrigation demands and water stress across the American West. The study found that, in the Columbia River Basin, the growing season is likely to lengthen for potatoes, but the potential for evaporation will also increase.
These factors will likely combine to increase
evapotranspiration—evaporation from soil and transpiration from plants.
"So, the longer growing season could actually benefit agriculture in
places like Washington and Idaho, but there will also be more stress on the
crops and higher water demand during peak growing season due to increased
temperatures and evaporative demand," he writes in an email.
Finally, there’s the issue of snow. In Idaho and Washington, irrigation is key to potato cultivation, and irrigation relies on snowpack. A 2018 study in Climate and Atmospheric Science found that, since the mid-20th century, April 1 snow water equivalent had fallen across the western United States by about 15–30 percent.
A 2020 study in Nature Climate Change examined projected changes
in snowpack runoff assuming warming of 4°F (2°C) and 7°F (4°C). The study
predicted shifts in runoff timing to earlier in the spring, affecting potatoes
and other irrigated crops in the western United States. Although not expected
to fare the worst among western U.S. river basins, the Columbia River was
projected to experience significant snowmelt deficits.
Growing spuds in a warmer climate
In
2014, the USDA ARS examined the effect of the primary driver of global
warming—carbon dioxide—on potato production. Carried out in
soil-plant-atmosphere research chambers, the study indicated that elevated
carbon dioxide levels could actually increase tuber yield, provided the plants
were properly irrigated. A 2016 study compiling research on carbon dioxide,
temperature, and water availability found that potato plants might use water
more efficiently and even slightly increase yields—provided temperatures don’t
climb too much.
In
the face of risk and uncertainty, one strategy for growers in a changing
climate is to partner with climate experts to identify opportunities for
increasing their resilience. Where should growers be thinking about adding
refrigerated storage in the next decade? Should a given farm be more concerned
with improving drainage to combat heavier spring downpours or improving
irrigation to cope with longer spans of hot summer days without rain?
Climate
information isn’t just about planning for the distant future, though. It can
also mitigate today’s threats. Houlihan, with the Wisconsin growers
association, has worked with NOAA on such a project funded by the Sectoral
Applications Research Program (SARP) in
NOAA’s Climate Program Office. The group helps decision makers better prepare
for climate impacts such as extreme floods and droughts.
Collaborating
on a SARP-funded project for growers of specialty
crops in the Midwest, Houlihan assembled a focus group of growers
and advisors to help develop a decision-support calendar for potato production
in the event of drought. Released in August 2020, the calendar addresses
management decisions for potato crops year-round—from aquifer recharging in the
winter months through harvesting the following autumn. Each month, the calendar
offers advice on what problems to watch for, and how to deal with them.
To help potato producers deal with those threats, NOAA’s Climate Program Office has partnered with other agencies and institutions to offer season-specific guidance through the National Drought Mitigation Center at the University of Nebraska.
Each season, potato farmers can turn to NOAA-sponsored data products to better spot and mitigate drought-related issues at that time of year. Among the products are the drought monitor of current and past conditions, soil-moisture maps for different layers of the soil, soil-temperature maps, and seasonal outlooks.
Alongside
crop-specific climate information like the Wisconsin potato calendar, part of
the solution to the climate challenges facing French fries might come from the
potato itself. Also a part of the USDA ARS, John Bamberg is the project leader
for the U.S. Potato Genebank in
Sturgeon Bay, Wisconsin. He and his team search the genomes of wild potato
species for traits that will prove useful in domesticated varieties.
In one wild species, Solanum microdontum, Bamberg found genes conferring resistance to potato greening, a trait Novy is working to incorporate into a domestic cultivar. He’s also found a useful wild potato relative in the Four Corners region of the American Southwest.
The
species, Solanum jamesii, may be instrumental in warding
off problems ranging from drought to nematodes to freezing. In collaboration
with University of Wisconsin-Madison professor Jiwan Palta, Bamberg is also
finding promising heat and drought resistance another wild species, Solanum kurtzianum.
For
over 700 years, from 600 to 1300 CE, Ancestral Pueblo people resided at Mesa
Verde in southwestern Colorado. The desirable qualities of Solanum jamesii, a wild potato from the Four Corners
region, prompts Bamberg to wonder whether human selection centuries ago drove
the characteristics of some of today’s wild potato species. CC license by
Flickr users Jerry and Pat Donaho.
Though
it might be tempting to assume that some cool-weather potato threats will
retreat in a warming climate, Bamberg expresses caution, saying, “I think it’s
safe to say if climate is changing, it could make anything be worse—any
disease, pest, or stress.”
Even
with a wealth of wild genes at their disposal, potato breeders must consider
multiple priorities, Bamberg explains. “Decades ago, when late blight was
really a bad problem in this country, I went to a big convention and one
colleague stood up and said, ’The problem is not resistance to late blight. We
have plenty of resistance to late blight, but we don’t have it in the kind of
potatoes that meet the super-high-quality standards of the American consumer.’
When you’re talking about French fries, it isn’t so simple as to find some kind
of potato that will stand up to heat and drought. It has to be incredibly high
quality and high yield.”
Focused on fries
In
April 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, The Original Hot Dog Shop closed.
The Pittsburgh Post-Gazette reported that the
restaurant donated seven tons of potatoes to charity. WQED|PBS documentary
maker Rick Sebak lamented the closure, saying the O’s fries were without
comparison.
For
fans of The O, it was the end of an era. Still, fries won’t disappear anytime
soon, even with climate uncertainty. Farmers, breeders, and climatologists are
keeping their eyes on the future of our favorite spuds.
Houlihan
reflects, “I think what you might see is that the demand maybe outweighs the
supply sometimes. So, you pay a little more. The price might go up. But I don’t
think it will get to the point where we’re not going to be able to order fries
anymore.”