Horrifying: Commonly Used Agricultural Herbicide Can Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier
By THE BIODESIGN INSTITUTE AT ASU
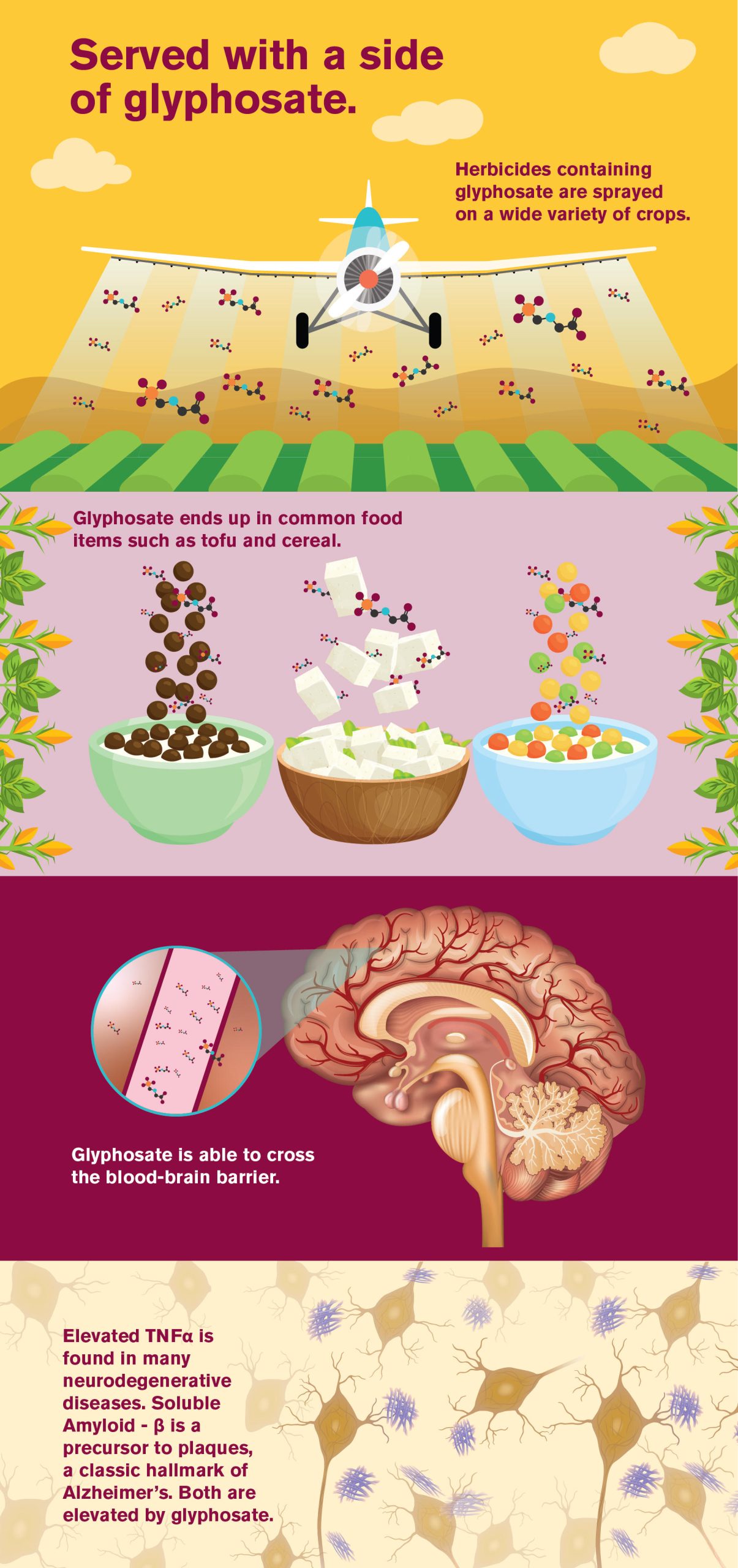
Scientists have demonstrated that glyphosate, a commonly used herbicide, can cross the blood-brain barrier. Researchers are exploring possible effects on the brain.
Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s are
among the most puzzling in medical research. The underlying causes of these
conditions might be anything from dietary influences and lifestyle decisions to
genetic factors and general cardiovascular health.
Various environmental pollutants have also been linked to the development or progression of neurological illness. Among them is glyphosate, a broad-spectrum herbicide. Glyphosate is a widely used herbicide that is used on agricultural crops all over the globe.
Joanna Winstone, Ramon Velazquez, and their colleagues at the Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen) investigate the consequences of glyphosate exposure on the brains of mice in a new study.
For the first
time, the study shows that glyphosate can successfully cross the
blood-brain barrier and enter the brain. Once there, it raises levels of a
key factor known as TNF-α (for tumor necrosis factor alpha).
TNF-α is a molecule with two faces. This pro-inflammatory cytokine
is essential in the neuroimmune system, functioning to boost immune response
and protect the brain. (Cytokines are a broad category of small proteins that
are essential for proper cell signaling.)
When levels of TNF-α are dysregulated, however, a host of diseases linked with neuroinflammation can result. Among these is Alzheimer’s disease.
The study further demonstrates in cell culture studies that glyphosate exposure appears to increase the production of soluble beta-amyloid (Aβ) and reduce the viability of neurons. The accumulation of Aβ, the sticky protein responsible for the formation of Aβ plaques, is one of the central diagnostic hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
Further evidence suggestive of potential hazards to neurological
health was observed when the researchers examined changes in gene expression
via RNA sequencing in the brains of mice following
glyphosate exposure.
These RNA transcripts hinted at disruptions in the expression of
genes related to neurodegenerative disease, including dysregulation of a class
of brain cells responsible for producing the myelin sheath critical for proper
neuronal communication. These cells, known as oligodendrocytes, are affected by
elevated levels of TNF-α.
“We find increases in TNF-α in the brain, following glyphosate
exposure,” Velazquez says. “While we examined AD pathology, this might have
implications for many neurodegenerative diseases, given that neuroinflammation
is seen in a variety of brain disorders.”
An
enigmatic disease. A path of destruction.
A hundred years have passed since the first diagnosis of
Alzheimer’s disease. Despite vast investments in research and drug development,
the affliction remains without effective treatment. A suite of therapies,
developed over many decades at extravagant cost, have one by one failed to
alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia. The
progression of the disease usually begins with mild memory loss. As the disease
develops, increasing confusion and a breakdown in communication abilities often
result, as the affliction attacks brain pathways involved in memory, language,
and thought.
Some 5.8 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s disease, as
of 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Research. Unlike heart disease or
cancer, the death toll for Alzheimer’s disease is on a frightening upward trajectory.
By 2040, the costs of the disease are projected to rise dramatically to between
$379 and more than $500 billion annually. The staggering toll of the illness is
currently projected to nearly triple to 14 million people by 2050.
The onset of symptoms typically occurs after age 60 and the risk
to individuals doubles every 5 years after age 65. Although genetics are
believed to play a role in some cases of Alzheimer’s disease, and a family
history of the disorder is considered a significant risk factor, environmental
factors are believed to play a significant role in the disease.
Researchers are trying to learn how genetic correlates may subtly
interact with environmental and other factors to decrease or enhance the
likelihood of developing the affliction. Some recent research suggests that
lifestyle changes, including proper physical activity, nutritious food, limited
alcohol consumption, and not smoking may help prevent or slow cognitive
decline, noting that brain and cardiovascular health are closely linked.
Toxic
effects: the jury is out
The new study examines the neurological effects of glyphosate, the
most ubiquitous herbicide in global use. Each year, around 250 million pounds
of glyphosate are applied to agricultural crops in the U.S. alone. Although the
chemical is regarded as generally safe for humans by the Environmental
Protection Agency and the European Food Safety Authority, researchers are
taking a second look.
Studies of acute herbicide use suggest they are non-harmful, but
little is known about possible long-term effects from prolonged exposure. One
issue of considerable concern is that glyphosate can cross the blood-brain
barrier, a layer of endothelial cells preventing dissolved substances in the
circulating bloodstream from readily passing into the extracellular fluid of
the central nervous system, where the brain’s neurons reside.
Potential risks to brain health posed by glyphosate should be
critically evaluated, particularly for those consistently exposed to the
herbicide. “The Alzheimer’s connection is that there’s a much higher prevalence
of Alzheimer’s disease in agricultural communities that are using this
chemical,” Winstone says. “We’re trying to establish a more
molecular-science-based link between the two.”
The study exposed mice to high doses of glyphosate, then detected
elevated levels of TNF-α in their brains. The researchers then exposed
extracted mouse neurons in Petri dishes to the same levels of glyphosate
detected in the brains of mice, observing elevated amyloid beta and cell death
in cortical neurons. Dysregulated oligodendrocyte RNA transcripts, which could
indicate disruption of myelination, were detected in brain tissue.
Taken together, the results demonstrate a correlation between
glyphosate exposure and classic symptoms of AD, though the authors stress that
much more work will be required before a causative link can be established.
Nevertheless, the widespread use of the chemical and the
disturbing correlates highlighted in the current study underscore the need for
intensified investigation. Among the pressing questions to be answered: how
does prolonged, low-dose exposure to glyphosate affect the brain; does
glyphosate act synergistically with other chemicals present in common
herbicides; and can glyphosate be detected post-mortem in patients who died of
Alzheimer’s disease?
On the horizon, new drugs designed to reduce TNF-α in the brain
are being explored, offering renewed hope for those with Alzheimer’s disease as
well as other neurodegenerative ailments.
Reference: “Glyphosate infiltrates the brain and increases
pro-inflammatory cytokine TNFα: implications for neurodegenerative disorders”
by Joanna K. Winstone, Khyatiben V. Pathak, Wendy Winslow, Ignazio S. Piras,
Jennifer White, Ritin Sharma, Matthew J. Huentelman, Patrick Pirrotte and Ramon
Velazquez, 28 July 2022, Journal of Inflammation.
DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02544-5