Powassan virus confirmed in Kent County man
The Rhode Island Department of Health (RIDOH) is reporting a confirmed case of the tick-borne Powassan virus disease (Powassan) detected in a Rhode Island resident. This resident is a male in his 70s who lives in Kent County. He began experiencing symptoms of Powassan in late January. He is recovering at home.
"With spring around the corner we all need to be thinking about tick prevention measures when outdoors," said Interim Director of Health Utpala Bandy, MD, MPH.
"Repel and reduce your exposure to ticks, check your body for ticks, and be sure to remove ticks if you find one on yourself, a family member, or a pet. Ticks are tiny. You may not be able to feel them or spot them right away. The sooner you find and remove them, the better your chances are at preventing the serious health issues caused by illnesses like Powassan and Lyme Disease."?
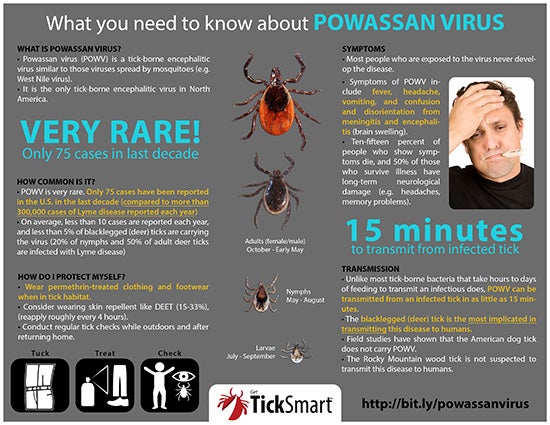
Powassan is a tick-borne disease that is found mostly in the Northeast and the Great Lakes region of the U.S. and in eastern Canada. Over 269 cases of Powassan have been reported in the United States in the past 10 years (2014-2023).
Powassan cases are rare, but the reported number of cases
has increased in recent years. In 2023, there were 25 cases of Powassan
reported in New England: 10 cases in Massachusetts, five cases in Connecticut,
five cases in Maine, three cases in New Hampshire, one case in Vermont, and one
case in Rhode Island.
Initial symptoms of Powassan include fever, headache, vomiting, and generalized weakness. The disease usually progresses to meningoencephalitis, which may include meningeal signs, altered mental status, seizures, aphasia (difficulty understanding or speaking), paresis (muscular weakness or paralysis), movement disorders, or cranial nerve palsies.
People
with severe Powassan disease often need to be hospitalized. There is no vaccine
or treatment for Powassan, so preventing exposure to ticks is the best strategy
to avoid this disease.
Rhode Islanders should take steps to prevent tick-borne
diseases, including Powassan and Lyme Disease, when spending time outdoors. In
mid-March RIDOH will launch its annual tick safety campaign with prevention
messages featured on television, radio, and social media. The Tick Free Rhode
Island campaign highlights the three keys to tick safety: repel, check, and
remove.
Repel – Keep ticks off you, your children, and pets by:
Avoiding wooded and brushy areas with high grass and
leaves. If you are going to be in a wooded area, walk in the center of the
trail to avoid contact with overgrown grass, brush, and leaves at the edges of
the trail.
Wearing long pants and long-sleeve shirts when outside.
Tucking your pants into your socks so ticks do not crawl
under your clothes.
Using an EPA-approved bug spray with the active ingredient
DEET (20-30% strength) on your skin or clothes. Check the product label to find
the concentration of DEET in a product. (Do not use bug spray with DEET on
infants under two months of age. Repellents should contain no more than 30%
DEET when used on children. Children should be careful not to rub their eyes
after bug spray has been applied on their skin. Wash children's' hands with
soap and water to remove any bug spray when they return indoors.)
Wearing light-colored clothing so you can see ticks more
easily.
Check – Check yourself, your children, and pets, for ticks
by:
Taking a shower as soon as you come inside if you have
been in grassy or wooded areas.
Doing a full-body tick check using a mirror; parents
should check their kids for ticks and pay special attention to the area in and
around the ears, in the belly button, behind the knees, between the legs,
around the waist, and in their hair.
Checking your pets for ticks as well because they can
bring ticks into the home.
Remove – Remove ticks from your body, as well as from
children and pets, if you find them.
Use a set of tweezers to remove the tick. Grasp the tick
as close to the skin as possible and pull straight up. ?If you don't have
tweezers, use your fingers with a tissue or rubber gloves.
For more information on Powassan, Lyme disease, and other
tick-borne diseases, visit health.ri.gov/ticks