Many US parents feel uninformed about avian flu risks, survey finds
Less than half of US parents think they have accurate
information about H5N1 avian flu, most don't know whether there has been a
human case in their state, 2 in 5 want the government to take more action to
prevent outbreaks, and 1 in 3 have taken steps to prevent infection in their
family, finds a report on the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott
Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's health.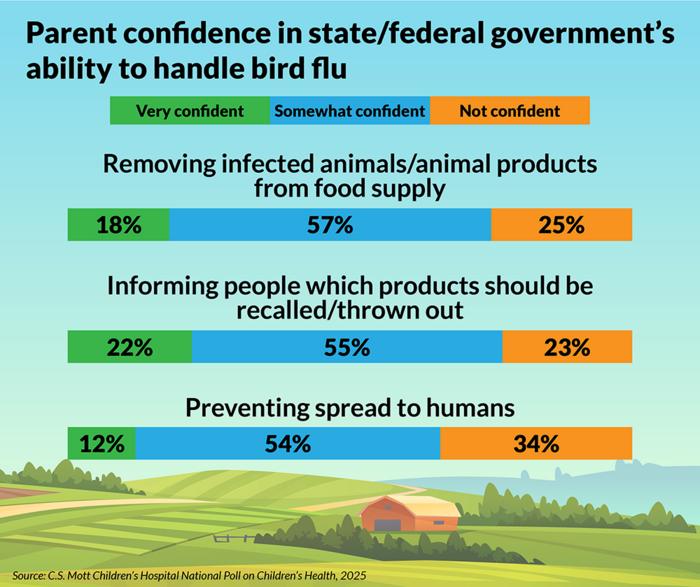
Sara Schultz, University of Michigan
The nationally representative report, based on the responses
of 2,021 parents of children aged 18 years and younger, also found that 1 in 5
respondents say media reports on the virus have been overblown.
In a news release,
Sarah Clark, MPH, poll codirector, said many parents hear about avian flu in
news reports but don't know if they should do anything about
it. "This report highlights the challenge for parents to keep track
of an emerging health situation and understand its potential threat to their
child's health," she said.
Current outbreak, risk
The current US outbreak of H5N1, which was first identified
in March 2024 when the virus was confirmed in dairy cattle, is widespread in
wild birds, which have transmitted the virus to poultry and cows. Seventy
people in the United States have been infected, most of whom worked with farm
animals, and one has died. But the risk to the general public remains low,
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
A new CDC study that evaluated the susceptibility to antiviral drugs of H5N1 clade 2.3.2.1c viruses (found in Cambodia) and 2.3.4.4b viruses (in the Americas) that were obtained from infected people in 2023 and 2024 found that all were susceptible to baloxavir, tivoxavir, pimodivir, oseltamivir, zanamivir, peramivir, laninamivir, and AV5080, with differing levels of effectiveness.
And except for two viruses isolated from Cambodia, all were
susceptible to M2 ion channel-blockers in cell culture–based tests. The
findings were published late last week in Emerging Infectious Diseases.
A third don't think government can contain virus
Sara Schultz, University of Michigan
Less than a quarter of parents surveyed say they're being
more careful about general hygiene, while 13% are more cautious about handling
eggs, chicken, and beef. Another 12% are avoiding contact with birds and other
wild animals, and 7% are eating fewer eggs and less chicken and beef.
"Some parents indicated they have cut back on eating
poultry products like eggs and chicken," Clark said. "However, as
long as eggs and meat are fully cooked, there’s no evidence that bird flu is
spread through these products."
Among the 68% of parents who haven't taken preventive
actions, their main reasons are that they already have good hygiene practices,
don't know the recommendations, or don't feel at risk.
Over 25% of respondents said they are very concerned about
avian flu spreading from animals to humans or humans to humans, but a third
don't have confidence in the government's ability to contain the virus.
Further, less than 20% expressed high confidence in the government's ability to
remove infected animals or products from the food supply, and 22% said they
were very confident it will share information about which products should be
recalled or discarded.
"There appears to be a gap in public confidence when it
comes to the national response to bird flu," Clark said.
"Misinformation and uncertainty can fuel anxiety, so it's critical that
health officials communicate transparently about containment efforts and food
safety to reassure families."
Risk to general public remains low
Parents' most common source of information was news reports,
followed by social media and online searches. Family or friends, a government
agency, or healthcare providers were less important sources.
Parents should teach their child to keep their hands away
from their face and remind them to wash their hands with soap and water after
touching birds and other animals at a petting zoo or a neighbor's backyard
chicken coop.
Sarah Clark, MPH
Clark says all parents should warn their children to avoid
contact with dead animals and animal droppings. She also recommends choosing
pasteurized milk. US and state officials have cautioned Americans against
consuming raw-milk products or feeding them to their pets.
"Parents should teach their child to keep their hands
away from their face and remind them to wash their hands with soap and water
after touching birds and other animals at a petting zoo or a neighbor's
backyard chicken coop," she said.
Avian flu detected in Belgian cats as outbreaks continue
on US poultry, dairy farms
Belgian authorities last week reported the country’s first
H5 avian flu detections in domestic cats, which lived on a poultry farm, and in
the United States, more detections were confirmed in poultry and dairy cattle
over the past few days.
First detection in Belgian cats; more in New Jersey
Belgium’s Federal Agency for the Safety of the Food Chain on
March 4 announced the
detection of H5 avian flu in two outdoor cats owned by a poultry farmer in East
Flanders. The farm had experienced an avian flu outbreak in poultry in the
middle of February.
The two cats were euthanized after experiencing severe
symptoms. Other cats at the farm remain healthy and show no symptoms.
Officials said the sick cats probably contracted the virus
by eating contaminated eggs or drinking contaminated water.
The infections in cats are Belgium’s first, though the
country has reported avian flu in other mammal species before, including foxes,
polecats, and domestic ferrets, which officials said were likely exposed
through eating bird carcasses or contaminated eggs.
In the United States, health officials in New Jersey have
reported four more H5 avian flu detections in domestic cats, all from the same
household as two recent detections. The
earlier detections involved a feral cat and an indoor-outdoor cat, with results
pending for others at the same property that were sick.
In a statement,
Karen DeMarco, MPH, health officer for Hunterdon County, said the H5 risk to
the general population remains low, but officials will continue to take
proactive steps to educate those who are at increased risk such as farm
workers.
“Health department staff are conducting daily symptom
monitoring with all individuals who had close contact with the affected
animals, and all are asymptomatic at this time,” she said.
More confirmations in US poultry and dairy cattle
Over the past week, the US Department of Agriculture (USDA)
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) has confirmed more H5N1
detections in poultry across
six states.
The virus struck more commercial farms, including a duck and
layer facilities in Indiana and turkey facilities in Ohio. In New York, birds
at four live markets tested positive, including those in Queens, Bronx, and
Richmond counties.
More detections in backyard poultry flocks were reported
from Oregon, Illinois, and Michigan.
Since outbreaks in US poultry began early 2022, the virus
has led to the loss of more than 166 million birds across all 50 states and
Puerto Rico.
Also today, APHIS confirmed 5
more H5N1 detections in US dairy cattle, all from California, raising the
national total to 983 and California’s total to 754.